Verilog Behavioral Code Encoder
Overview
- Verilog Behavioral Examples
- Verilog Behavioral Code Encoder Code
- Verilog Behavioral Code Encoder Software
The Viterbi algorithm is renowned as a maximum likelihood (ML) decoding technique for convolutional codes. The path memory unit in an (n,k,m) Viterbi Decoder is responsible for keeping track of the information bits associated with the surviving paths designated by the path metric unit. Viterbi decoders and binary convolutional codes are denoted by a three-tuple (n, k, m), where:
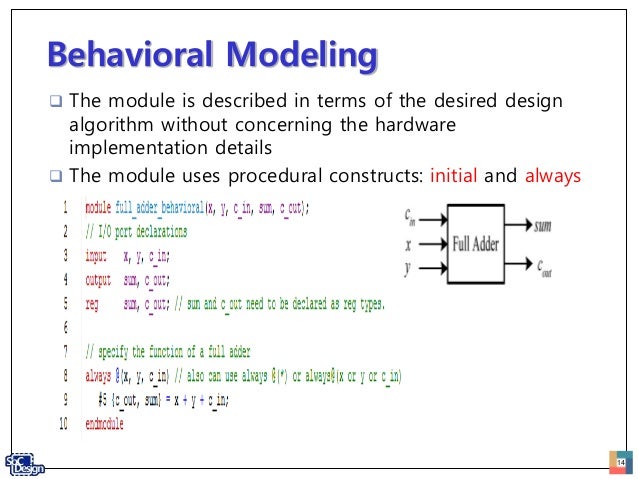
Verilog Behavioral Modeling. Feb-9-2014: Sequential Statement Groups: The begin - end keywords: Group several statements together. Cause the statements to be evaluated sequentially (one at a time) Any timing within the sequential groups is relative to the previous statement. VERILOG CODE 8 TO 3 ENCODER USING DATAFLOW MODELING STYLE resetall timescale from ELECTRONIC 1001 at Forman Christian College. Verilog code BCD counter; FSM OF UP/DOWN COUNTER; verilog code for updowncounter and testbench; Verilog Code for Ripple Counter; MUX AND CODERS. Verilog code for encoder and testbench; verilog code for decoder and testbench; verilog code for 4 bit mux and test bench; COMPARATORS. Verilog code for 2-bit Magnitude Comparator; Verilog code for.
- n output bits are generated whenever k input bits are received.
- k is the number of input sequences (and hence, the encoder consists of k shift registers).
- m designates the number of previous k-bit input blocks that must be memorized in the encoder.
Verilog Behavioral Examples
Trellis Diagram
A trellis diagram is typically used to visualize how the Viterbi Algorithm make Maximum Likelihood (ML) decoding decisions. An example trellis with the final ML path is shown below
Novel Path Memory Savings Technique

Viterbi decoders are typically FPGA/ASIC based and therefore have a upper bound on the size of the path memory. A novel approach to achieving path memory savings is proposed for Viterbi Decoders. A number of traceback Viterbi decoders using this path memory were successfully developed It is shown that Viterbi decoders using this storage efficient path memory unit require a smaller chip area and achieves a faster decoding time without loss of decoding performance. A Viterbi decoder utilizing this novel path memory achieves savings of 20% in storage for (n,1,m) codes, and <=20% for general (n,k,m) codes without loss of decoding performance. There is also a similar increase decoding performance with the novel path memory.
| Efficient Viterbi Decoder Architecture Traceback Procedure |
|---|
| 1. Initialize Data Structures |
| 1.1. Initialize the trellis stage pointer to zero. Initialize the path memory write pointer to zero. Initialize the traceback pointer to zero. Initialize the decoded symbol counter to zero. |
| 1.2. Initialize the path metric for the known initial state to zero, with the remaining 2M –1 path metrics to their maximum value. Go to step 2. |
| --- |
| 2. Compute Path Metrics and Survivors |
| 2.1. Increment the trellis stage pointer, and the path memory pointer. |
| 2.2. For every trellis node, compute 2k path metrics by summing the path metrics from nodes at the previous stage to the corresponding branch metrics computed at the present stage. |
| 2.3. Compare the 2k paths and select the path with the minimum path metric as the surviving path, all other incoming paths to the trellis node are no longer considered. If there is a tie between path metrics, the algorithm selects one path. |
| 1.1. Store the path metric. Update the surviving path by shifting in the surviving backward label to the left hand side of the path memory register where the surviving path currently terminates. |
| 2.4. If the path memory write pointer is < T then go to step 2.1, else if the path memory write pointer = T go to step 3 |
| --- |
| 3. Traceback and Output Decision |
| 3.1. Set the traceback pointer equal to T. Determine the traceback start state number as the state that corresponds to the minimum path metric. |
| 3.2. The state number and the traceback pointer are combined into a row-column address used to index path memory. Use this address to read a backward label from path memory. A predecessor state on the surviving path is then determined by use of the traceback mapping function. Decrement the traceback pointer. If the traceback pointer >1 repeat step 3.2, else go to step 3.3. |
| 3.3. Produce a decoded symbol. |
| 3.3.1. Category 1 - A decoder decision is made for one symbol by selecting the rightmost elements of the traceback mapping register. |
| 3.3.2. Category 2 - A decoder decision is made for one symbol by selecting a combination of specific elements from the backward label read from path memory and the rightmost elements of the traceback mapping register4. |
| 3.4. Increment the decoded symbol counter. If the decoded symbol count < N, go to step 2.1, else finish. |
Im just starting to learn how to code in Verilog. Can anyone help me figure out how to implement the following code in verilog using one-hot encoding
I tried changing the parameters to:
However, ive read that this is not a good implementations.

Verilog Behavioral Code Encoder Code
1 Answer
Some of the advantages of onehot encoding in FSMs are as follows:
- Low switching activity. Since only single bit is switched at a time, the power consumption is less and it is less prone to glitches.
- Simplified encoding. One can determine the state just by looking at the bit position of '1' in the current state variable.
The disadvantage of this technique is that it requires more number of flops. So, if one has a FSM with 10 different states, one needs 10 flops, while one needs only 4 flops when using decimal encoding.
Coming to your question, it is simple to change to onehot encoded FSM. One needs to implement a case statement based on the position of 1 in the currentstate variable. The code snippet can be implemented as follows:
A simple example is available at this link and explanation is over here. Cummings paper is also a good source for more info.
Verilog Behavioral Code Encoder Software
EDIT: As @Greg pointed out, it was a copy-paste error. A combinational block must use blocking assignments.
Greg